The idea of creating the petrochemical industry in Iran is more than 50 years old. In the texts and laws of the 1950s, provisions, and terms such as “Chemical industries derived from oil” or “chemicals derived from oil and natural gas” either “gas derivatives” and “chemical fertilizers” were adopted Without the word “petrochemical” being used.
The first article of association of Iran National Oil Company approved on November 26, 1952, mentioned establishing a company named National Iran Oil Company for exploration, extraction, and exploitation such as refining, transportation, export, and distribution of oil and its derivatives.
In the bill of the second construction program, credits for the formation of chemical fertilizer factories were predicted and the first step in the establishment of petroleum chemical industries in Khuzestan was taken in June 1958.
In the report of June 1960 of the Khuzestan Development Program, the title “Petrochemicals” was mentioned for the first time.
At the end of the 1950s, the Ministry of Industries and Mines paid attention to the construction of a chemical fertilizer plant from natural gas in Marvdasht, Fars. In 1958, the contract for the construction of the factory was signed and its implementation was entrusted to “Chemical Fertilizer Company“. This factory was put into operation in 1963.
In 1964, the law on the formation of the National Petrochemical Industries Company under the cover of the National Iranian Oil Company and the concentration of all activities related to the creation and development of petrochemical industries in this company was approved. In 1965, the Petrochemical Industries Development Law was also ratified.
The petrochemical industry in Iran has about 9% of the world’s oil reserves and 16% of the world’s gas reserves, due to the use of the country’s relative advantages and the creation of added value, has been the focus of the country’s policymakers and planners since the beginning. Although the development of this industry requires huge capital and educated manpower, its importance in the growth of the national economy has paved the way for the expansion of this industry.
The process of development and evolution of the petrochemical industry in Iran includes six specific stages:
- Genesis (1963)
- Initial expansion (1964 to 1978)
- Recession (1978 to 1988)
- Revival and reconstruction (1989 to 1999)
- Mutation, stabilization, and development (1999 to 2008)
- Privatization and transformation into governance and regulatory organization (2009-till now)

Click on the link below to read more:
History of the petrochemical industry of Iran
In the past decades, polymer materials have had many applications in the textile industry. The use of polymers has enabled the production of fibers with various characteristics, such as high thermal resistance, high strength, etc., in this industry.
Polypropylene fibers and granules, polyester fibers, nylon, and acrylic fibers can be mentioned among the synthetic polymers widely used in textile industries.
In the following, we mention the textile industry‘s most widely used grades of polymer materials.
A. Polypropylene in textile
Polypropylene fibers, which are prepared through the polymerization of propylene in the form of a linear polymer, are called PP for short and have many applications in the textile industry. The following are the most commonly used grades of polypropylene in the textile industry.
1. Polypropylene homopolymer HP 552R
HP552R polypropylene is a homopolymer polypropylene with high flow ability, which is used to produce staple, CF, and BCF fibers. HP552R material is used for medium and high-speed spinning melt.
Although polypropylene homopolymer has higher tensile strength and hardness than polypropylene copolymer, its main weakness is its impact resistance. In fact, polypropylene homopolymer is more fragile than polypropylene copolymer.
- Characteristics of polypropylene 552R: Homogeneity, stable extrusion
- Application of 552R materials: Woven fabrics, diapers, medical hygiene applications, and wet wipes are suitable.
2. Polypropylene homopolymer HP 510L
HP 510L polypropylene or 510L material is an extrusion grade homopolymer polypropylene with medium flow ability, which is used to produce belts, monofilaments, films, and sheets. Even though polypropylene homopolymer has higher tensile strength and hardness than polypropylene copolymer, its main weakness is its impact resistance.
Due to its high crystallinity and low impact resistance, polypropylene homopolymer is a very suitable option for textile applications or thin sheets and films. In this application, tensile strength is needed, and weak impact resistance is not an issue.
- Features of polypropylene 510L: Good mechanical properties and flow
- Application of 510L materials: rope, sacks, belts, etc.
3. Polypropylene homopolymer C30S
Polypropylene C30S or C30S material is an extrusion grade homopolymer polypropylene with medium flow ability, which is used to produce belts, monofilaments, films, and sheets. Due to its high crystallinity and low impact resistance, polypropylene homopolymer is a very suitable option for textile applications or thin sheets and films.
In this application, tensile strength is needed more, and weak impact resistance is not essential. Films stretched in two directions, and polypropylene fibers and types of sacks and belts are among the applications of polypropylene homopolymer.
- Characteristic of C30S polypropylene: Grade in contact with food, good flow ability, and good processability
- Application of C30S materials: Film thread, sheet

Click on the link below to read more:
The use of polymer materials in the textile industry
Today, various products are made of plastic, especially BL3 polyethylene granules. It can be said that products such as plastic containers, bottles, bags, and all kinds of plastic toys are considered products you can see around you. Meanwhile, the common feature of all these products is that plastic is one of the most important materials used for their production. The mentioned plastic products are usually made of granules; in this regard, in order to examine the granules, it should be noted that granules are one of the most popular thermoplastic materials that have many applications in industries today.
Currently, there are different types of granules, and each of these models has specific grades. Each of these grades has unique uses and features, and this has increased their usage rate. In this article, we intend to introduce you to BL3 granules and state what points you should pay attention to if you intend to buy BL3 granules.
Granule is a light and resistant thermoplastic with a variable crystal structure used in various industries. This polymer is considered one of the most widely used plastics in the world. According to statistics, we produce tens of millions of tons of granules worldwide annually.
According to customers’ needs, granules are used in different industries to make additional products such as films, pipes, all kinds of plastic parts, packaging materials, car parts, electric cables, etc.
Examination of types of granules
In line with the examination of the types of granules, it should be said that these products are classified into different groups based on their density and branching. Among the most common kinds of granules available in the market, the following can be mentioned:
- Low-density branch model granule
- Linear granules with low density
- High-density branch model granule
- Very high molecular weight granule
- Cross granules
In addition to the mentioned items, which are among the most common types of granules, granules are produced in other models, which include the following models:
- Medium-density granules
- Very low-density granule
- High molecular weight granules
- Very low molecular weight granules
- Chlorine granules
bl3 is one of the types of air granules that are in the category of high-density products.
In order to get familiar with BL3 polyethylene granule, you should know that this product is a cheap thermoplastic that has a linear structure with little branching.
One of the essential features of this product is that its production process is carried out at a specific temperature and pressure. The temperature required to produce this category of products is between 70 and 300 degrees Celsius, and the pressure required to produce this product is between 10 and 80 bar.
To get familiar with BL3 granules, you should know that two techniques are mainly used to produce this product:
- Slurry polymerization
- Gas phase polymerization

Click on the link below to read more:
Purchase of BL3 polyethylene granules
The advantages of using polymer materials over other chemicals in the medical industry have made them one of the most used in this industry. In general, the use of polymers in medicine, in the manufacture of medical equipment, and also in medical implants are widely used today.
In this article, due to the wide range of applications of polymer materials in medical equipment and medical implants, we will continue to examine these materials in medical implants.
The consumables used in the body can be classified into metal materials, ceramic materials, polymer materials, and composite materials; among the materials used for biological purposes, polymer materials have a special place. Biomaterials are compounds of natural or synthetic origin that have various applications in the medical industry.
Biomaterials to replace tissue, restore tissue function with different methods, improve tissue function, correct and eliminate disorders, etc., are used in various ways, such as in suture thread, bone plates, replacement joints, heart valves, intraocular lenses, etc.
In the following, we first take a look at the characteristics of polymer biomaterials. In addition, since biomaterials are primarily used in orthopedic implants, in the rest of this article, we will examine their use in cases such as joint replacement, bone replacement, bone filler, joint connection, fracture repair, etc.
In terms of function in the body, polymeric biomaterials are divided into two categories. Polymers in medicine are bio-compatible, and they are also sustainable. The other category is biocompatible and biodegradable, which means they slowly break down in the body and disappear.
Biomaterials, whether biodegradable or non-biodegradable (stable), should have a series of physical-mechanical characteristics when they come into contact with body tissue or the living environment in general, depending on whether They use it.
The most important things polymers in medicine must have are tensile strength, bending strength, compressibility, impact ability, fatigue, creep, tearing, corrosion, abrasion, and cracking due to impact, as well as factors such as not being toxic or pathogenic. Immune reactions and blood clotting should not occur if the object is unstable in the body, the components resulting from its destruction should not be toxic or harmful, etc.
The most critical applications of Polymers in medicine in medical implants
- Bone filler using polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA)
- Replacing joints using polyethylene (PE)
- Vertebral bone ossification using polyether ether ketone (PEEK)
- Artificial heart valves using polyurethane (PU)

Click on the link below to read more:
Polymers in Medicine
Granular sulfur fertilizer is one of the best-selling types of agricultural fertilizers, which has the right percentage of sulfur and is very effective for plants; like other phosphate fertilizers, the way to use this fertilizer is before planting.
The use of fertilizers in the agricultural industry has been of great interest today. In addition to suitable soil, light, and water conditions, the trees also need the use of fertilizers for proper and excellent fruiting. One of the most suitable fertilizers for strengthening the soil of trees and plants is granular sulfur fertilizer, which has the highest sulfur content of 58%.
One of the most important and widely used elements in plants is the use of sulfur, which is of great importance for plant growth. Sulfur can be prepared as fertilizer in all kinds of agricultural fertilizers, which is used according to the needs of plants and trees.
In addition to controlling some fungal pathogens such as powdery mildew, the use of granular sulfur is beneficial for improving saline and alkaline soils, reducing the local pH of calcareous soils, providing sulfate needed by plants, and increasing the solubility of low-use and high-use elements.
The plant needs a significant amount of sulfate for sufficient growth. By using granular sulfur, in addition to the local reduction of the pH of lime-alkali soils, the sulfate required for plant growth is also provided.
One of the most important benefits of granulated sulfur is to increase the elements and micronutrients of the soil and control a number of pathogenic factors such as white fungus and disinfecting the soil, helping the health of the environment, etc. The use of granular sulfur activates beneficial microbes in the soil because the organic substances present in the granular sulfur fertilizer facilitate biological oxidation in the soil.
The use of granulated pollen improves the physical and chemical properties of the soil by 30-60.%. You can easily add granular sulfur fertilizer to the soil using fertilizer spreaders.
Supplying plant and soil needs is one of the benefits of granular sulfur fertilizer, which, in addition to reducing the local pH of calcareous soils, provides the necessary growth materials for the soil. According to the type of fertilizer, it is better to use granular sulfur fertilizer before planting the crop
Autumn season is one of the most appropriate times to use granular sulfur fertilizer in agricultural soils. To conclude, it is better for farmers to test the soil before using this type of fertilizer to assess the plant’s needs. The appropriate amount of fertilizer for each hectare is about 400 to 600 kg, which is added to the soil using a fertilizer spreader. To combine with the soil, it is better to penetrate the fertilizer deep into the soil by plowing. The amount of fertilizer can vary according to the type of planting, this amount for greenhouse crops is about 250 grams per square meter, which should be well mixed with the soil.

Click on the link below to read more:
Granular sulfur
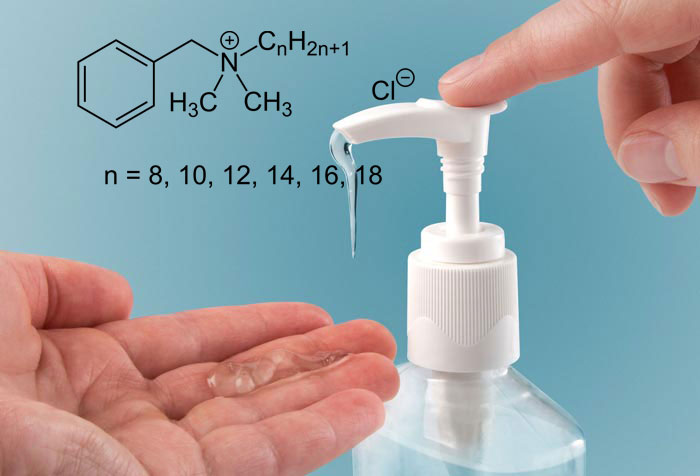
Benzalkonium chloride is a type of cationic surfactant that is considered a non-oxidative biocide. This biocide is based on quaternary ammonium compounds, which are effective even in low concentrations.
This biocide is soluble in water and is effective in preventing the activity of some vital bacterial enzymes (enzymes involved in glycolysis respiration), as well as releasing the contents of the bacteria into the environment. By increasing the contact time and concentration of the biocide, compounds containing nitrogen and phosphorus in the bacterial cell enter the surrounding environment, and thus the bacteria are destroyed. This material has the property of dispersing, spreading, and destroying sludge and algae.
Using this biocide may cause foaming. In order to make this biocide more effective, it is recommended to use it together with non-oxidizing isothiazolinone biocide.
This biocide can be used in all open or closed-circuit cooling and cooling systems, firefighting systems, ponds and pools, water transmission lines, etc.
Equipment and containers should be made of stainless steel, 316 steel, 304 steel, polypropylene, polyethylene, PVC, or Teflon.
- It has a wide range of applications.
- The product is liquid and easy to use. (injection)
- It has a good spreading property, which means it is an effective dispersant.
- Its effectiveness in a different range of pH.
Benzalkonium chloride (BAC, BAK, BKC, BZK), known as alkylidene methyl benzyl ammonium chloride (ADBAC), is a type of cationic surfactant. It is an organic salt classified as a quaternary ammonium compound. ADBACs are used in three main categories: as a biocide, cationic surfactant, and phase transfer agent. methylammonium.
Depending on the purity, benzalkonium chloride ranges from colorless to pale yellow (impure). Benzalkonium chloride is easily soluble in ethanol and acetone, but its solubility is slower in water. Its aqueous solutions should be neutral to slightly alkaline. Concentrated solutions have a bitter taste and a faint smell like almonds. Standard concentrates are produced as 50% and 80% by-weight solutions. A 50% solution is completely blue.
Other names of dimethyl benzalkonium chloride
Benzalkonium chlorides (BACs), also known as alkyl dimethyl benzyl ammonium chlorides, quaternary alkyl dimethyl (phenylmethyl) ammonium chlorides, quartz disinfectants, BACs, benzalkonium chlorides, and QACs.
Properties of dimethyl benzalkonium chloride
Benzalkonium chlorides (BAC) due to their broad-spectrum antimicrobial properties against bacteria, fungi, and viruses. Benzalkonium chloride is a broad-spectrum quaternary ammonium antibacterial agent. This material is cationically charged and creates an antibacterial effect by absorbing the negatively charged bacterial membrane.
Gram-positive bacteria are generally more sensitive than gram-negative bacteria. Its activity depends on the concentration of surfactant and also on the concentration of bacteria at the moment of injection. Activity is largely unaffected by pH but increases significantly at higher temperatures and longer exposure times.
Click on the link below to read more:
Benzalkonium Chloride
Lubecut is one of the derivatives of crude oil and is one of the cuts of the distillation tower of oil refineries. Lubecut has two types, heavy and light, each used in the oil industry.
According to experts, only a good lubricant (oil, grease, etc.) can guarantee the optimal operation of machine equipment. About 55% of premature equipment failures are due to inappropriate lubricants in the industry. Lubricants are substances used to reduce friction and prevent the wear of moving metal parts in contact with each other.
This article will discuss lube cuts, the main component, and raw materials for motor oil production.
lubecut is the main component and raw material for producing motor oil, which makes up about 85-95% of it. Usually, by refining crude oil, only a few percent of hydrocarbon materials with atomic numbers between 20 and 50 are obtained, which are suitable for use as lubricants. It is one of the oil cuts (products) called oil cut or lube cut. This cut is actually the oil refinery feed.
Lubecut is converted into oil from crude oil refineries then in the oil refineries, the refining operation is performed on the lubecut. Finally, a substance called base oil, the main ingredient of motor, industrial, and grease oils, is prepared from it.
As mentioned, the base oil is produced from lubecut. Basically, lubricants consist of two components: base oil and additives. After adding additives to the base oil, the final lubricant is obtained.
Production of base oil from lubecut by performing the refining process, in addition to separating non-hydrocarbon compounds, hydrocarbon compounds are also divided according to their boiling point, which is derived from the number of carbon atoms in their molecules. Usually, by refining crude oil, only a few percent of hydrocarbon materials with atomic numbers between 20 and 50 are formed, which are suitable for use as lubricants. It should be noted that the type and degree of viscosity of the base oil obtained depend on the lubecut input to the oil refinery. Therefore, to produce different base oils, it is necessary to use different lubecut.

Click on the link below to read more:
Lubecut
Polyamide, commonly known as nylon, is a thermoplastic polymer introduced to the industry in the mid-1930s by DuPont engineers.
Since then, polyamide has been a suitable material in most industries, such as automobile manufacturing, the food industry, sports equipment, the carpet industry, and most importantly, the textile and clothing industry.
Polyamides are usually converted into fibers to be used. If you are willing to get familiar with the types of simple polyamide available in the industry, their characteristics, and their use, this article will help you.
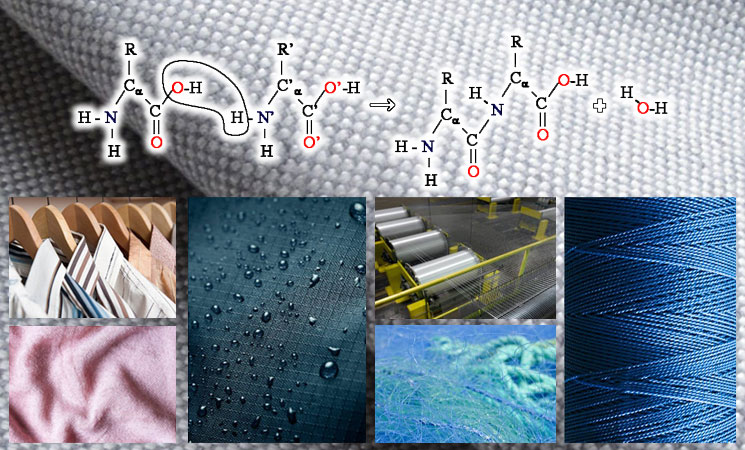
Simple polyamide is a polymer that includes amide groups (R-CO-NH-R) as an essential part of the polymer chain. These amide groups keep repeating. A simple polyamide with a high molecular weight is usually called nylon.
Simple polyamide is a crystalline polymer formed from the combination of a diacid and a diamine. In the mixture of these two monomers, the linking of molecules takes place through the formation of amide groups. The most crucial simple polyamide is nylon, which is considered a very flexible material. Today, simple polyamide is produced in the form of thin and long threads.
At first, simple polyamide was used to make parachutes and ropes in World War II, but later in the 40s, it gained its place in the clothing and fabric market. Due to its elasticity, this material achieved great success in the hosiery industry and quickly replaced silk stockings, which were expensive and less flexible.
Today, simple polyamide is used for many sticky clothes, such as women’s socks, pantyhose, swimwear, underwear, and high-quality and comfortable sports clothes.
Types of simple polyamide are usually named with a unique number placed in front of the polyamide name, and each one has its unique characteristics. In this section, we will introduce the types of simple polyamide.
1- Polyamide 6.6
This polyamide melts at a very high temperature and is resistant to abrasion. Hence, this polyamide works very well for making various car parts. But polyamide 6.6 also has its disadvantages. For example, it absorbs a lot of water, and its chemical resistance is weak. Since this simple polyamide is strong and has high heat resistance, it can also act as a thermoplastic.
2- Polyamide 6
This type of simple polyamide is somewhat crystalline and is very resistant to erosion. This simple polyamide is also resistant to chemicals such as acids and alkyl. However, the tensile strength of polyamide 6 decreases due to a water absorption of 2.4%.
3- Polyamide 6.10
Another type of simple polyamide is polyamide 6.10, which is resistant to chemicals and acids. This simple polyamide is more robust than almost any other nylon, so much so that it doesn’t break even under a salt like zinc chloride. This class of simple polyamide, which absorbs relatively less water, also shows good resistance in wet environments.
Click on the link below to read more:
Polyamide
The term bitumen refers to a viscous, non-crystalline, black or dark brown substance that can be dissolved in organic solutions, such as toluene and carbon disulfide, and has adhesive and waterproof properties.
This substance is generally composed of hydrocarbons, which usually contain 80% carbon and 15% hydrogen. Other residues in this viscous material include oxygen, sulfur, nitrogen, and various metals. Bitumen can be obtained from various sources and occurs naturally. The amount of this material in crude oil may vary, but the more normal range is between 25% and 40%, while the usual range is 15% to 80%.
Broad classification for crude oils
- Bitumen base
- Paraffin base
- Bitumen and paraffin base
Depending on the type of crude oil, bitumen exists either as a colloidal dispersion or in a solid state. During the refinement process, the oil-to-particle ratio changes as petroleum oils are removed by distillation. Instead of these particles being scattered and relatively few in number, they are getting closer to each other and increasing in size.
Typically, oil tar is a colloidal dispersion of black solids (hydrocarbons) at the end of the distillation process. There is also a yellow-brown petroleum liquid known as the melted fraction in which asphaltenes are dispersed. Also, to be present in asphaltenes as a stabilizing agent, another group of hydrocarbons are known as resins.
This substance is found in nature in many forms, from the hard, easily crushed bitumen found in rock asphalt to the softer, more viscous material found in oil sands and so-called asphalt lakes. This material is usually mixed with various proportions of mineral or vegetable impurities that must be extracted before use, and is effectively used as an engineering material.
It may also be found as asphaltite, natural bitumen without various impurities in solution in carbon disulfide. Natural bitumen, like petroleum, occurs as a result of the specific breakdown of marine debris. This occurs over thousands of years through porous rocks such as limestone or sandstone, often transported by volcanic action.
Separation of bitumen and tar coal is important. Although coal tar is black and sticky like this material, it is derived from the carbon of coal and therefore has very different chemical properties.
Engineering projects everywhere in the world, from the construction of transcontinental highways to the waterproofing of flat roof surfaces, rely on the special properties of bitumen. Crude oil processed by the oil industry provides a small percentage of this vital substance.
The special properties of bitumen are used in a variety of engineering projects around the world, from the construction of transcontinental highways to the waterproofing of flat roof surfaces. It is important to note that crude oil is only a small percentage of this essential substance produced by the oil industry
- It is a strong and durable glue-like material that holds together a wide variety of other materials without matching their properties. Durability is essential for large engineering projects such as roads and waterways that must last 20 years or more.
- Due to its insoluble nature, it is an effective waterproofing insulator. The material is also resistant to the majority of acids, alkalis, and salts. It does not contaminate water, which makes it an excellent choice for use in water flow lines.
- This material gives controllable flexibility to the mineral aggregate mix, which is why most of the total annual production is used in road construction. It is available almost worldwide at economical cost.

Click on the link below to read more:
Bitumen
Polyvinyl chloride, or PVC, is a universal polymer with many applications (pipes, floor coverings, cable insulation, bottles, packaging foils, medical products, etc.).
The reason for the widespread use of this polymer is its low cost, suitable physical and chemical properties, and good resistance to environmental conditions. In the following, we will discuss the properties, structure, production method, burning, applications, and other things about this polymer.
Polyvinyl chloride, or PVC, is a thermoplastic polymer with strength, stiffness, and good resistance to corrosion and chemicals. This product is initially produced as a white powder, and additional processes are performed based on the type of use expected from it. For example, in cases where flexibility is needed, a plasticizer should be added to it. It is a fragile white compound produced in two complex and flexible types during production in its pure state and without additives. This substance is a combination of crude oil derivatives and chlorine gas produced during the polymerization process.
The following table shows some of the physical and chemical properties of this product:
| Name of the material |
Polyvinyl chloride
|
| Molecular formula |
n (C2H3Cl) |
| Ayupak’s name |
poly(1-chloroethylene) |
| Molar mass |
(62/498).n g/mol |
| Appearance |
white powder
|
| Melting point |
100 to 260 °C |
| density |
1.45-1.35 grams per cubic centimeter
|
They are three main types of polyvinyl chloride:
- UPVC (Un Plasticized Poly Vinyl Chloride)
- PPVC (Plasticized Poly Vinyl Chloride)
- OPVC (Oriented Poly Vinyl Chloride)
This material is a type of modern thermoplastic (heated plastic), one of the main derivatives of crude oil and table salt. Its physical properties are different from PVC, and it is made into a profile in the production process. This combination has many applications in construction for making pipes, fittings, door and window profiles, etc. The ingredients of UPVC include the following.

Click on the link below to read more:
Polyvinyl Chloride - PVC













